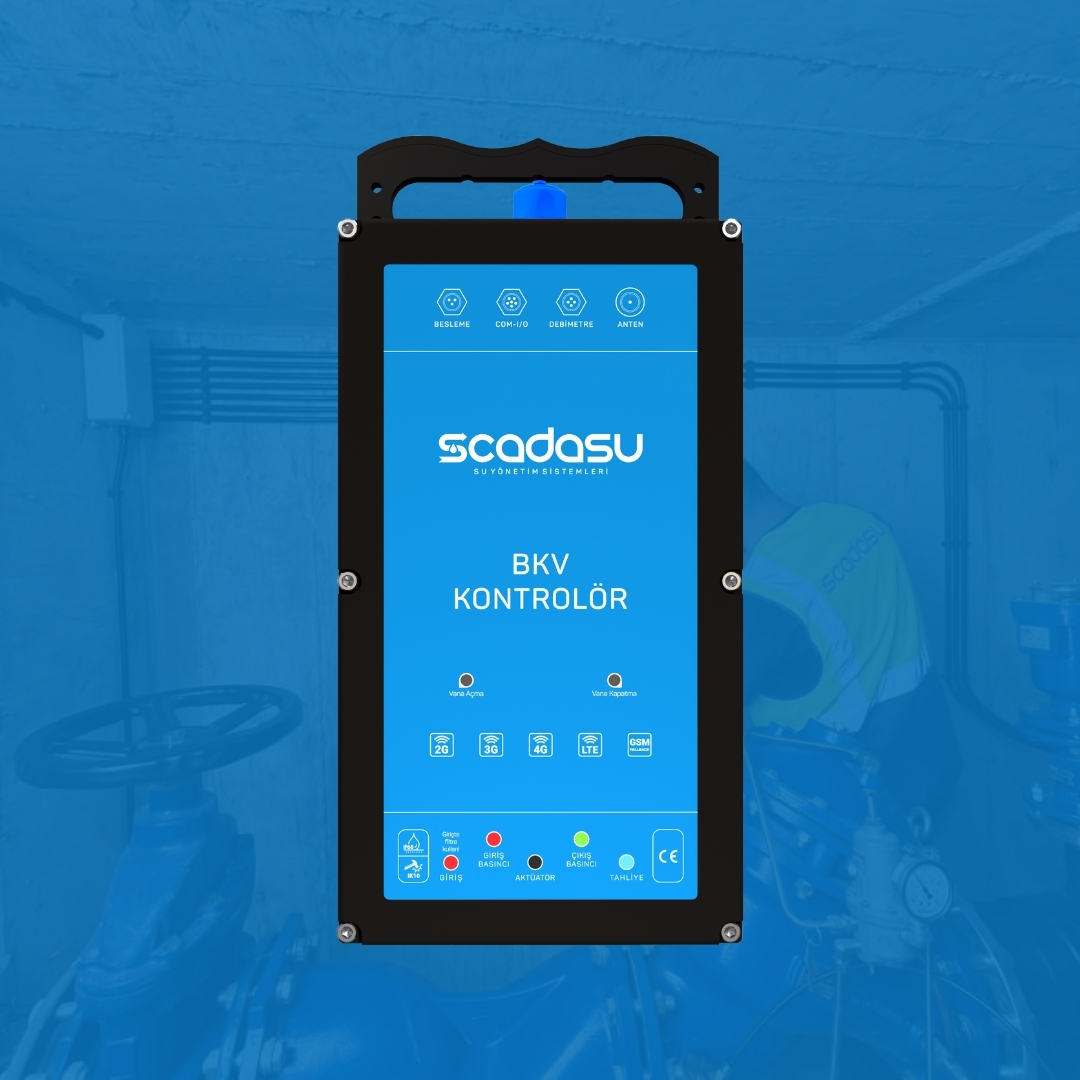
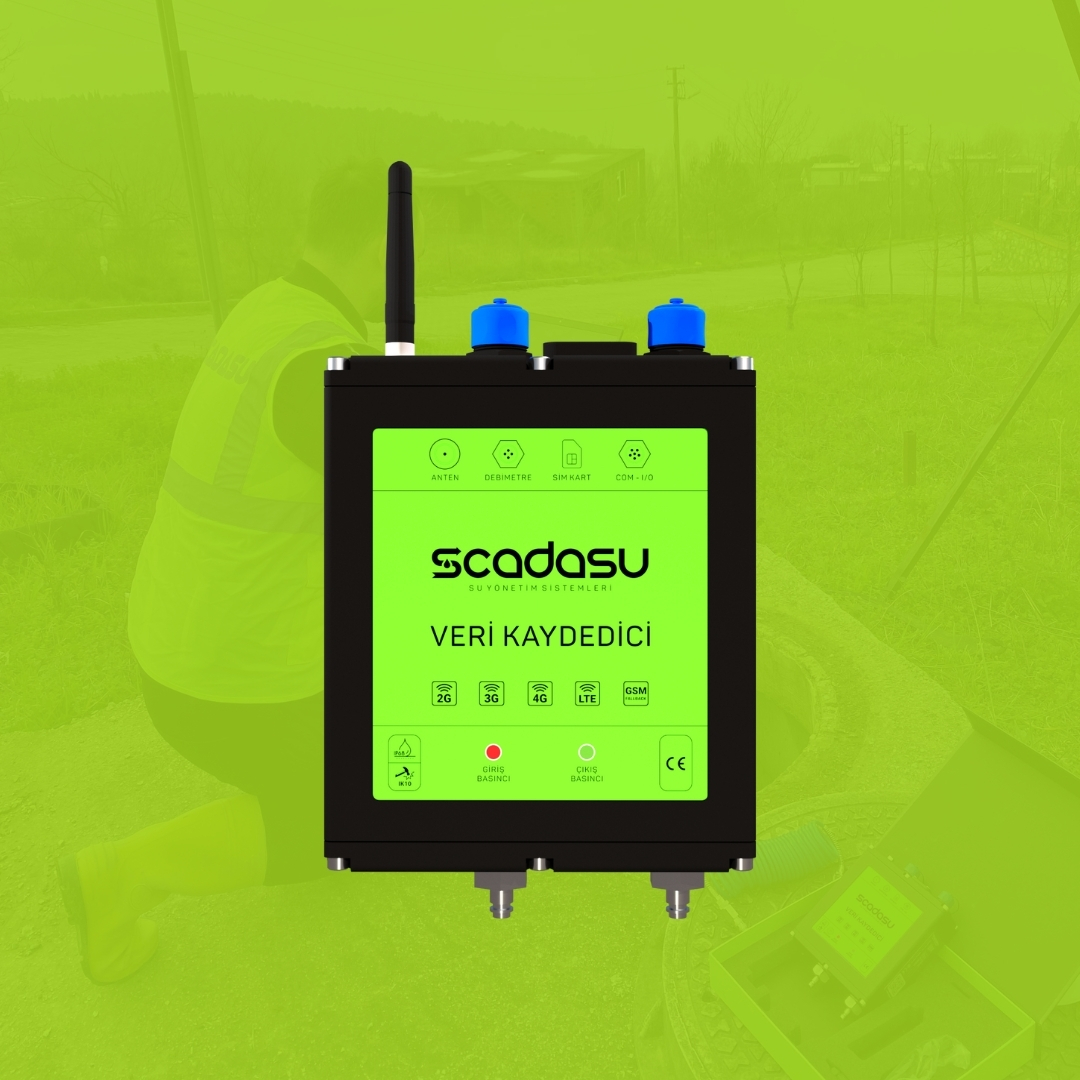
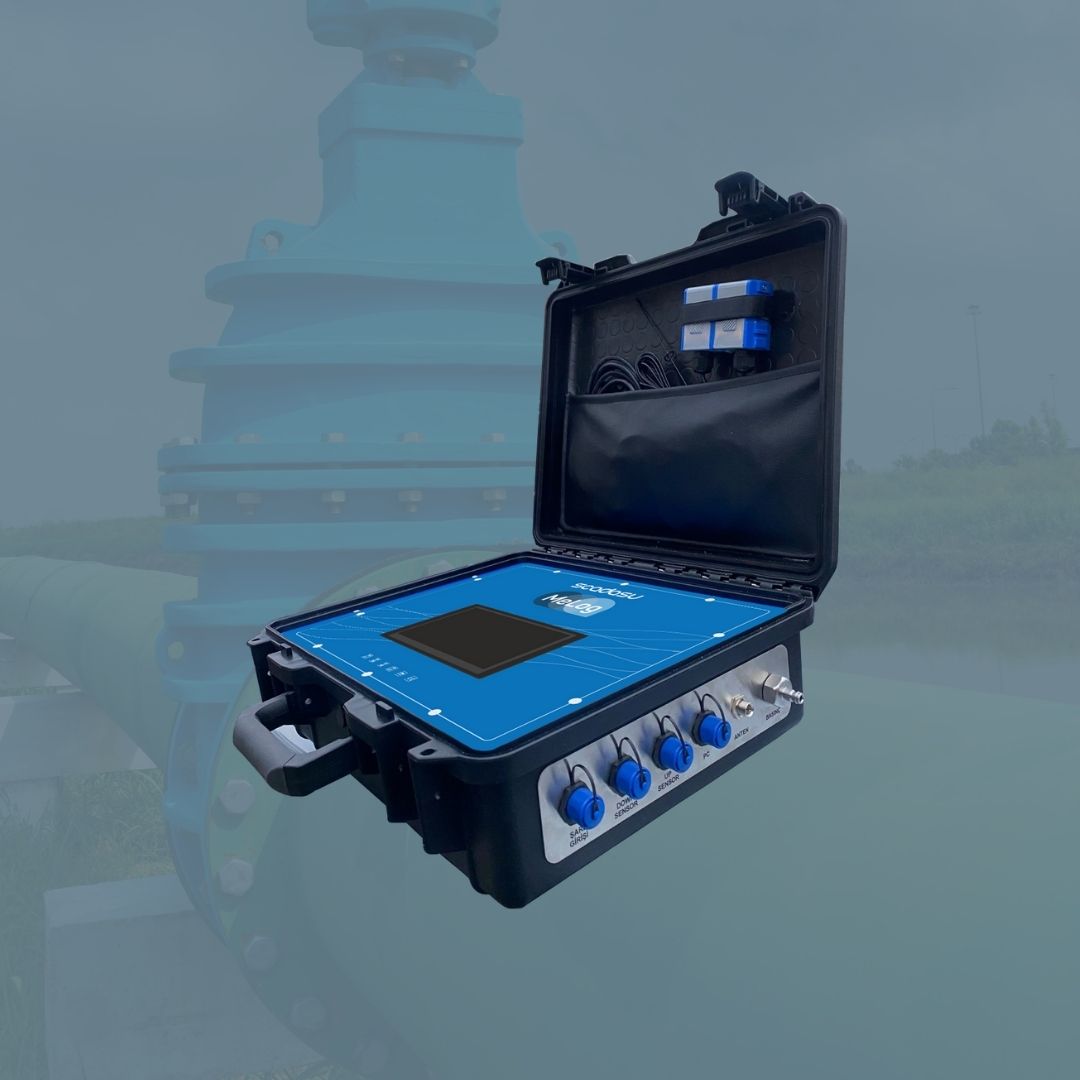
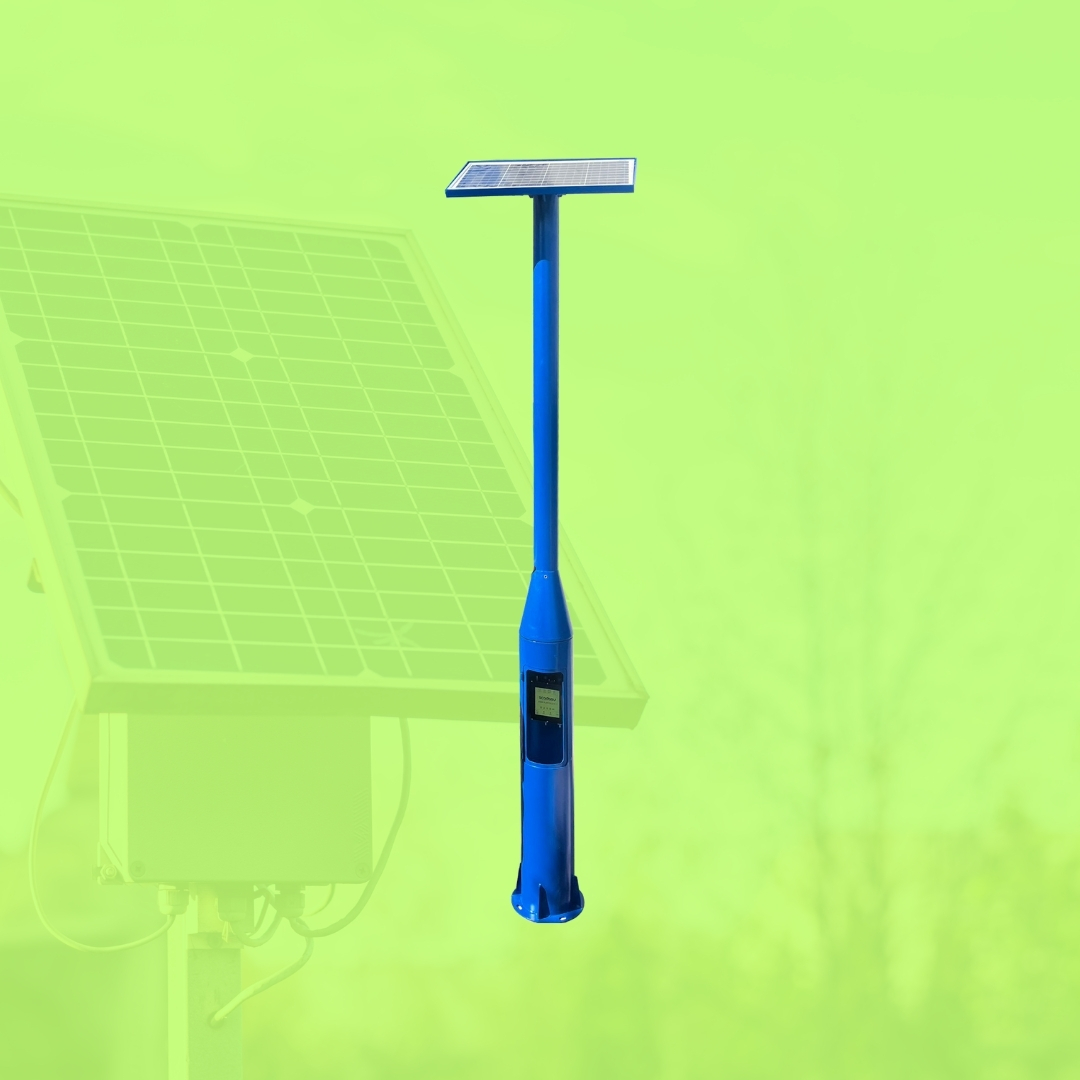
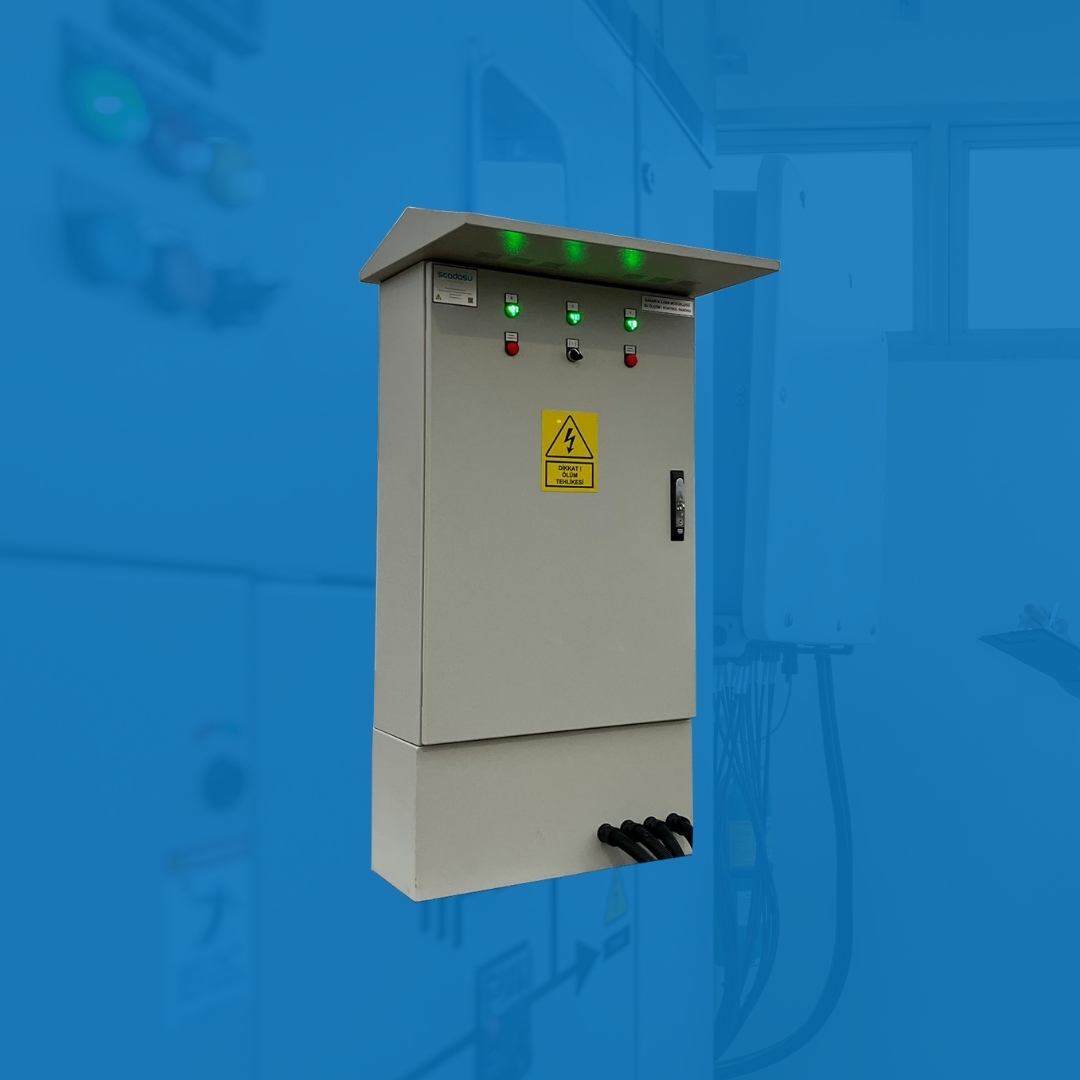
Su kayıplarını azaltın, operasyonel maliyetleri düşürün ve şebekenizi uçtan uca kontrol altına alın.
AKILLI SU YÖNETİMİ
Hakkımızda
SCADASU, şehirlerin su yönetimini daha akıllı, daha verimli ve sürdürülebilir hale getirmek için geliştirilmiş kapsamlı bir teknoloji ekosistemidir. Entegre çözümlerimizle su kayıplarını azaltır, operasyonları optimize eder ve suyun her damlasını kontrol edilebilir bir değere dönüştürürüz.
0+
Yıllık Su Yönetimi Deneyimi0+
Belediye & Su İdaresi0M m3+
Kazanılmış Su Kaybı
Su Şebekenizi Akıllı Teknoloji ile Dönüştürün
SCADASU, su kayıplarını azaltan, şebekeyi görünür kılan ve operasyonları dijitalleştiren entegre bir su yönetimi platformudur. Akıllı teknolojiler, SCADA otomasyonu ve SUİS su işletim sistemi tek çatı altında birleşir.
- Daha az kayıp, daha fazla kontrol.
- Gerçek zamanlı izleme.
- Sürdürülebilir şehirler için veri odaklı yönetim.
- Uçtan uca entegrasyon.
Bütüncül, Veriye Dayalı ve Güvenilir ve Entegre Teknolojiler
Şehirlerin su yönetim süreçlerini fizibiliteden projelendirmeye, uygulamadan işletmeye kadar uçtan uca dijitalleştiriyoruz.
30+
Belediye İşbirliği
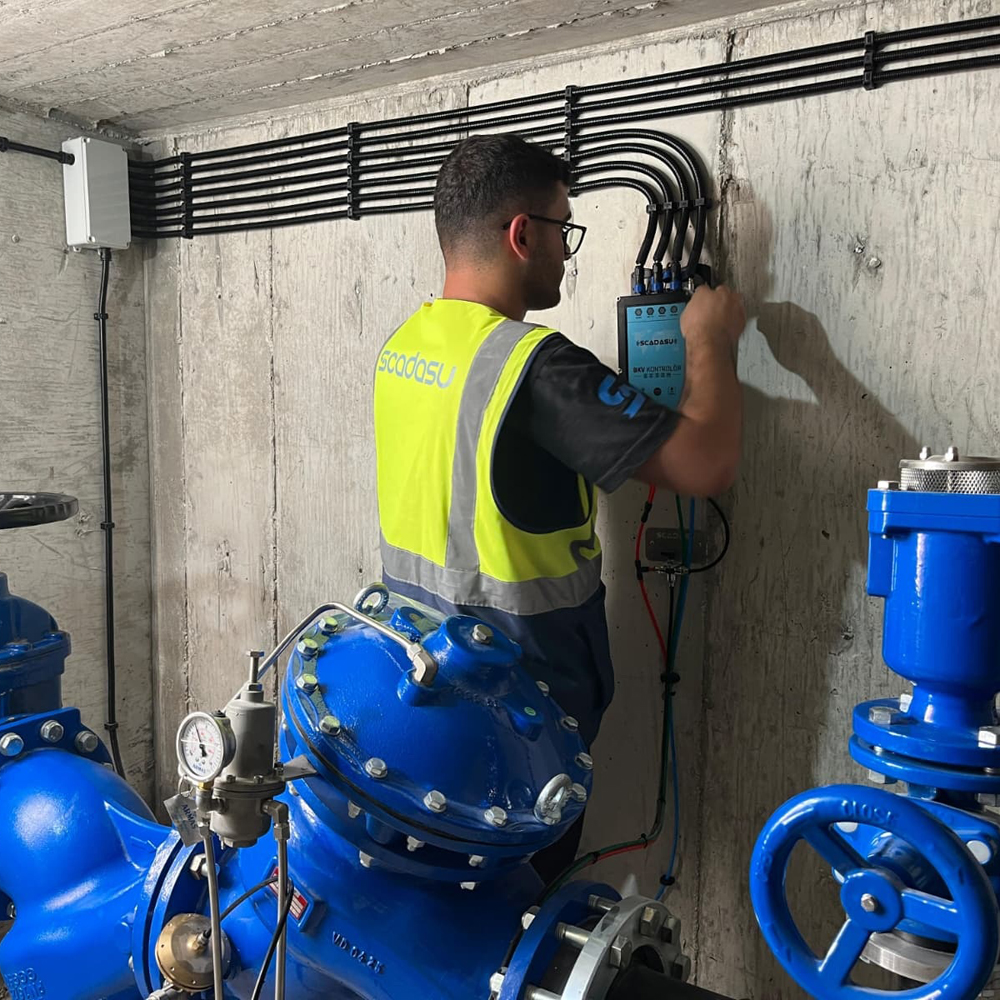


Neden SCADASU?
Uzman Mühendislik Ekibi
Hidrolik, SCADA ve Su Yönetiminde profesyonellerden oluşan güçlü bir ekip
Veriye Dayalı Çözümler
Gerçek zamanlı ve gelişmiş izleme altyapısıyla su kayıplarına hızlı çözüm
Entegre Su Yönetimi Ekosistemi
SCADA, CBS, ABYS gibi sistemler tek çatı altında ve tam entegre
Uygulama ve Hızlı Entegrasyon
Geçmiş tecrübelerle optimize edilmiş donanım ve yazılım avantajları
Sürdürülebilir Yaklaşım
İşletilebilir ve Genişleyebilir yaklaşımla Su Yönetim Projeleri
7/24 Destek ve Operasyon
Proje sonrası teknik destek, sistem izleme ve periyodik analiz hizmetleri
Yaşanabilir Şehirler İçin Güvenilir ve Entegre Teknolojiler
Şehirlerin su yönetimini daha görünür, daha verimli ve tamamen kontrol edilebilir hale getiren ileri teknoloji çözümler geliştiriyoruz.
SCADASU ile suyun her adımını yönetiyor, şehirlerin altyapısını dijital ve sürdürülebilir hale getiriyoruz.
Murat HAYKIR - Yönetim Kurulu ÜyesiMühendislik gücümüzle şebekeleri analiz ediyor, basıncı optimize ediyor ve uzun ömürlü su çözümleri uyguluyoruz.
Mehmet SERTÇELİK - Yönetim Kurulu ÜyesiSu kayıplarını azaltan, maliyetleri düşüren ve şehirlerin dayanıklılığını artıran entegre çözümler geliştiriyoruz.
Fatih KARAMEHMETOĞLU - Yönetim Kurulu ÜyesiSıkça Sorulan Sorular
Arayın: +90 264 777 1 301
Çözüm için
Çalışma Saatleri
Pzt - Cum 08:30 - 18:00
E-posta Adresimiz
info@scadasu.com